Set Up Your China or Singapore Company
– Fast, Simple, and Expertly Guided
Looking to expand your business into China or Singapore? Paul Hype Page & Co. makes it easy. With 20+ years of cross-border experience and an on-the-ground team in Asia, we help you register your company, stay compliant, and scale confidently.
Why China Remains a Prime Destination for Business Expansion
With decades of consistent growth since its reform era in the 1970s, China stands today as a leading global economic hub. Its dynamic market environment, strategic global positioning, and investor-friendly policies make it a prime choice for companies looking to scale and expand internationally.
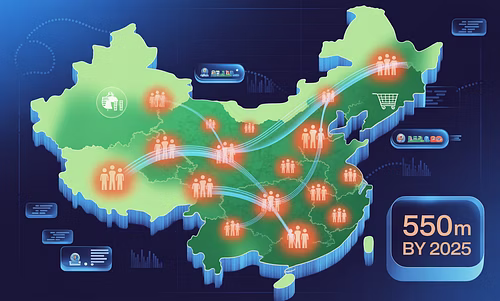
Unmatched Market Access
Access to 1.4B+ consumers with growing purchasing power. Tap into the world’s largest middle class that’s expected to reach 550 million by 2025.
Strategic Location for Global Trade
Perfect gateway to the entire Asia-Pacific region. Leverage China’s strategic position in global supply chains and its extensive trade agreements.

Economic Growth
Tap into the world’s fastest-growing major economy with government support, booming export-import activity, and opportunities across tech, finance, agriculture, and manufacturing
Expanding into China Starts with the Right Partner — Why Paul Hype Page & Co.?


Types of Companies You Can Register in China

Consulting Company (WFOE)
For companies offering services in or from China.

Trading Company (WFOE)
For companies importing into or exporting out of China.

Representative Office (RO)
For non-profits doing marketing, support, etc…
Comprehensive Business Solutions for Your Expansion into China
Timelines for Key Activities in China
| Choose Company Type | Decide on WFOE, JV, or RO |
| Reserve Company Name | 3–5 working days |
| Submit Documents | Includes office address, passport, and business plan |
| Get Business License | 2–4 weeks |
| Register for Taxes | Required to operate legally, 1-2 weeks |
| Open a Bank Account | 1–2 weeks |
| Social Security Registration | Set up pension, medical etc, 1-2 weeks |
| Apply for Extra Permits | For industries like trade or manufacturing (1–3 months) |
What Our Clients Say
Ready to Expand with Confidence?
We make your market entry seamless—from incorporation to daily operations. No stress. No guesswork. Just strategic execution, backed by decades of regional experience in the complex Chinese and Singaporean markets.
20+ |
2000+ |
100% |
|---|---|---|
| Years Experience | Companies Served | Success Rate |
| Decades of expertise navigating Asian business environments | Successful business incorporations across Asia | For legal tax optimization strategies |

Why Register a Company in China?
China is not only the world’s most populous country but also a market that is rapidly evolving, making it a prime location for foreign companies to invest. Here are some reasons why registering a company in China makes sense:
- Vast Consumer Market: With over 1.4 billion people, China represents an enormous consumer base. Whether in e-commerce, manufacturing, or technology, there are significant opportunities for businesses to tap into this market.
- Strategic Location: China’s geographic position in Asia makes it a hub for international trade, with access to other markets in Southeast Asia, Europe, and beyond.
- Growing Economy: China’s rapid economic growth and rising middle class continue to fuel consumer demand and create opportunities for foreign businesses.
- Government Incentives: China offers favorable incentives to foreign investors, including tax breaks, subsidies, and investment allowances for businesses in certain sectors and regions.
Despite these advantages, doing business in China requires a strong understanding of the legal and regulatory landscape. This is where Paul Hype Page & Co. can help. Our expertise in business incorporation in China can guide you through each step, ensuring compliance with all legal requirements.
If you’re ready to start your journey, contact us today for a consultation, and we’ll help you navigate China’s business registration process with ease!
Types of Companies You Can Register in China
When setting up a business in China, there are several options available for foreign investors. Understanding the different company structures is crucial to ensuring that you choose the one that best suits your business goals. The most common types of entities that foreign investors establish in China are:
1. Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE)
A Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise (WFOE) is the most popular choice for foreign investors in China. This type of business allows full ownership by the foreign entity, providing complete control over the company’s operations. It is an ideal option for businesses that want to operate independently in China without relying on a Chinese partner.
Advantages: Full control over business operations, profits, and decision-making.
Disadvantages: Higher setup costs, more extensive compliance, and regulatory requirements.
2. Joint Venture (JV)
A Joint Venture (JV) involves a partnership between a foreign company and a local Chinese entity. This arrangement allows foreign businesses to enter the market with local expertise and networks. However, JVs often require shared decision-making, which may lead to disagreements.
Advantages: Access to local networks, knowledge, and resources.
Disadvantages: Shared control and profits, potential conflicts with the local partner.
3. Representative Office (RO)
A Representative Office (RO) is a non-commercial entity established by a foreign company to engage in activities such as marketing, research, and liaison. While an RO allows a company to gain a presence in China, it cannot directly conduct commercial activities or generate revenue.
Advantages: Simpler to set up, ideal for market research and establishing contacts.
Disadvantages: Limited scope of activities, cannot generate revenue.
4. Foreign Invested Enterprise (FIE)
A Foreign Invested Enterprise (FIE) encompasses all foreign-invested companies in China, including WFOEs and JVs. This broad category includes entities that allow foreign ownership, including equity and cooperative joint ventures.
Key Government Authorities Involved in Company Registration in China

To successfully register a company in China, foreign investors must interact with several key government departments and authorities. Understanding the role of these authorities is essential to navigate the registration process efficiently.
State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR)
The SAMR is the primary body responsible for overseeing the registration of companies in China. It manages the China Company Registry and handles the registration of foreign-invested entities, including WFOEs and JVs. The SAMR ensures that all businesses comply with Chinese commercial laws and regulations.
China State Taxation Administration (STA)
After registering your company, you must apply for tax registration with the China State Taxation Administration (STA). The STA ensures businesses comply with China’s tax policies, including VAT, corporate tax, and other local taxes.
The Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM)
Foreign-invested enterprises in China often need approval from the Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM), particularly for industries that are sensitive or highly regulated. MOFCOM’s approval is especially important for companies wishing to set up in restricted sectors or regions.
Local Commerce Bureaus
Depending on the city in which you choose to set up your business, you may also need to engage with local commerce bureaus. These regional authorities will handle specific requirements for business registration and licensing.
The Process of Registering a Company in China
The process of registering a company in China involves several important steps. Each step must be completed correctly to ensure your company operates legally and effectively in the Chinese market.
Step 1: Choose the Type of Company
The first step is to decide on the type of entity you wish to establish. Whether you opt for a WFOE, Joint Venture, or Representative Office, this decision will impact the level of control you have over the business, the regulations you must comply with, and the costs involved.
Step 2: Name Reservation
Your company name must be unique and conform to Chinese naming conventions. The China business registry will verify the availability of the name you choose. If your name is approved, it will be officially reserved for your use. Ensure that the name reflects your business scope and is free from sensitive or restricted terms.
- Timeline: Name reservation typically takes 3-5 working days.
Step 3: Submit Company Registration Documents
After name reservation, you will need to submit the necessary documents to the SAMR or local authorities for company registration. These documents may include:
- Application form
- Proof of your company’s legal address in China
- Copies of your passport or identification for the legal representative
- Business plan and information about your business activities
Step 4: Obtain Business License
Once your application is approved, you will receive a business license from the China company registration authority. This document officially allows you to operate a business in China and includes your company registration number and business scope.
- Timeline: Business license approval can take 2-4 weeks, depending on the type of company and location.
Step 5: Register for Taxes
You must register your company with the China State Taxation Administration (STA) to obtain a tax registration number. This process includes submitting your business license and other relevant documents to the local tax bureau.
Step 6: Open a Bank Account
Opening a corporate bank account is required for all registered companies in China. To open an account, you will need to submit your business license, company registration number, and identification documents.
- Timeline: Bank account setup can take 1-2 weeks.
Step 7: Social Security Registration
Foreign-invested companies are required to contribute to China’s social security system. This includes pension, medical insurance, and unemployment insurance for your employees. You will need to register with the local social security bureau.
Step 8: Apply for Licenses and Permits
Depending on the type of business you plan to conduct, you may need additional permits. For instance, China trade registration is required for businesses engaging in import and export activities, while environmental permits may be necessary for manufacturing companies.
Timeline: Additional permits can take 1-3 months to secure, depending on the business activity.
Cities and Zones for Specific Business Activities

China is a large and diverse country, and different cities and regions offer varying advantages depending on the nature of your business. Here is an overview of some key areas for different types of business activities:
Beijing: Government and Technology Hub
- Industry Focus: Technology, innovation, government contracting.
- Advantages: Proximity to government agencies, research centers, and state-owned enterprises.
Shanghai: Financial and Trading Center
- Industry Focus: Financial services, import/export, e-commerce.
- Advantages: Access to global markets, major port, and strong infrastructure for international trade.
Shenzhen: Tech and Manufacturing Hub
- Industry Focus: Technology, manufacturing, electronics.
- Advantages: Proximity to Hong Kong, low-cost manufacturing facilities, access to the tech market.
Guangzhou: International Trade and E-Commerce
- Industry Focus: E-commerce, import/export, retail.
- Advantages: Hub for trade with Southeast Asia, proximity to key shipping routes.
Chengdu: Emerging Investment Zone
- Industry Focus: Technology, services, automotive, and clean energy.
- Advantages: Lower costs of operation, growing consumer market, and attractive government incentives.
Xi’an: Research and Development
- Industry Focus: Aerospace, defense, and high-tech research.
Advantages: Strong governmental support for research and development, low-cost labor.
Timelines for Key Activities in China
Here’s a timeline to help you plan and understand the process better:
| Activity | Timeline |
| Name Reservation | 3-5 working days |
| Company Registration Submission | 1-2 weeks |
| Business License Approval | 2-4 weeks |
| Tax Registration | 1-2 weeks |
| Bank Account Setup | 1-2 weeks |
| Social Security Registration | 1-2 weeks |
| Additional Permits/Approvals | 1-3 months |
FAQs
Simply book a free consultation with our team. We’ll walk you through the steps, timelines, and documents needed for your company registration and China visa application.
We offer a full suite of services including bank account setup, bookkeeping, staffing advice, and compliance with the China company registry and visa offices in Singapore.
Yes. WFOEs are subject to China’s corporate tax system. However, you may qualify for VAT rebates or China tax refunds depending on your business activities.
Most common types include consulting, e-commerce, trading with China suppliers, import/export, and sourcing from China wholesale networks. Some industries may require additional licenses.
Yes. Once your WFOE is established and has proper licensing, it can sponsor you (as the legal representative or shareholder) for a Z Visa and residence permit.
On average, company registration takes 4–8 weeks depending on the city and business scope. The visa and residence permit process usually takes an additional 3–6 weeks.
The Z Visa allows you to enter China for work purposes. After entry, you must convert it into a residence permit, which allows you to live and work in China long-term.
Not necessarily. We can assist you remotely with the incorporation and document preparation. However, you will need to be in China eventually for in-person steps like the Z Visa activation and residence permit registration.
Yes, Singaporeans can fully own a company in China through a WFOE structure. There is no requirement for a local Chinese partner.
A WFOE (Wholly Foreign-Owned Enterprise) is a legal business entity in China fully owned by foreigners. It gives you full control over your business operations and is ideal for trading, consulting, or manufacturing.

















