Introduction
The rise of digital banking, fintech innovations, and online financial transactions has transformed the global financial ecosystem. However, this rapid digitization has also made the financial sector a prime target for cybercriminals. With cyber threats evolving in sophistication and scale, financial institutions must prioritize cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive data, customer assets, and financial stability.
This article explores the biggest cybersecurity risks in the financial sector and how banks, fintech companies, and regulatory bodies are working to mitigate these threats.
The Growing Cybersecurity Risks in Finance
1. Rising Cybercrime in Financial Services
The financial sector is a lucrative target for cybercriminals due to the vast amounts of money, personal data, and confidential transactions processed daily. Cyberattacks, including phishing scams, ransomware, and identity theft, have become more frequent and costly.
According to industry reports, financial institutions face an average of 300 times more cyberattacks than other industries, making cybersecurity a critical concern. A single data breach can result in millions of dollars in losses, legal liabilities, and damage to a company’s reputation.
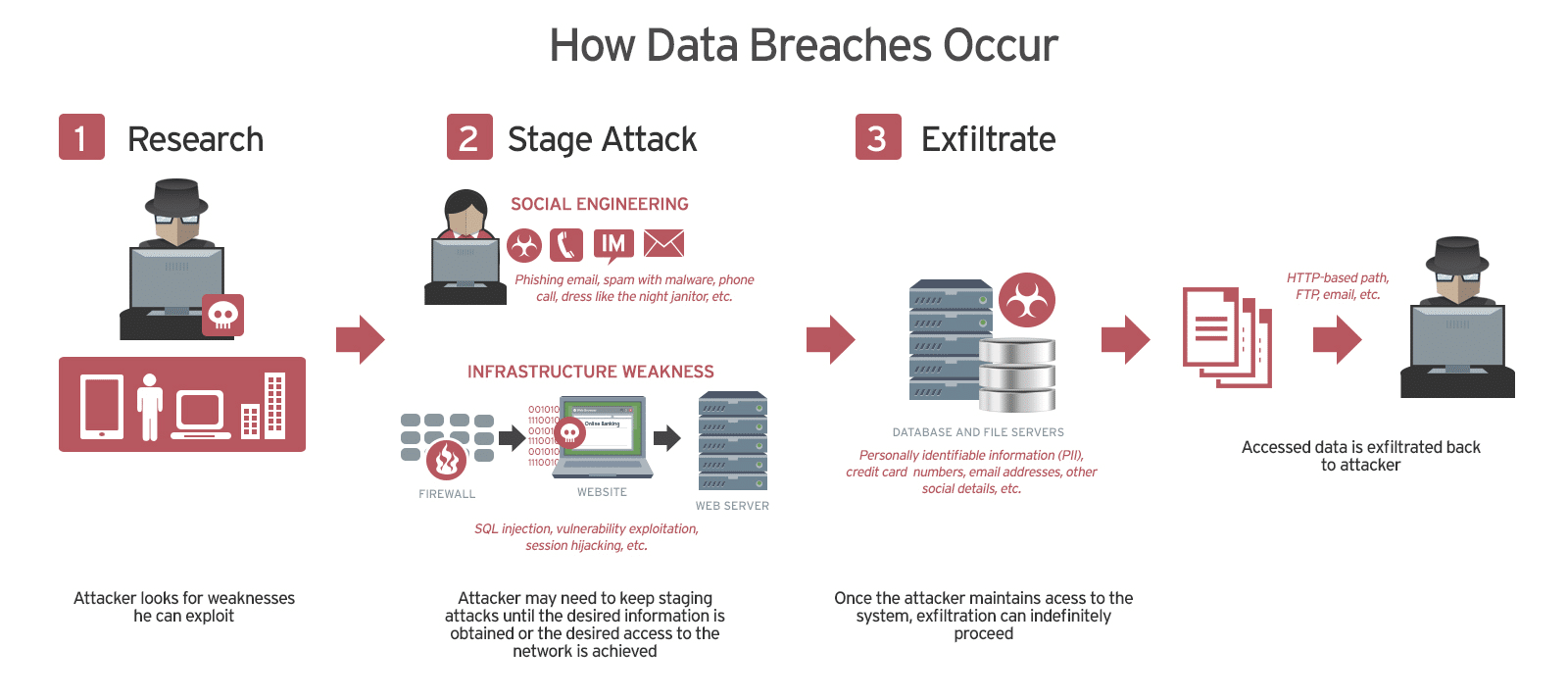
2. Data Breaches and Identity Theft
Financial institutions collect and store large volumes of customer data, including personally identifiable information (PII) such as Social Security numbers, credit card details, and banking credentials. If not adequately protected, this sensitive data can be stolen and misused by cybercriminals for fraudulent transactions or identity theft.
One of the most notable data breaches occurred in 2017 when a major U.S. credit reporting agency suffered a breach that exposed the personal information of over 147 million people. This incident highlighted the vulnerabilities in financial cybersecurity and the need for stronger data protection measures.
3. Ransomware and Digital Extortion
Ransomware attacks have surged, with hackers targeting banks and financial firms by encrypting critical data and demanding payment for its release. The impact of ransomware can be devastating, disrupting banking operations, freezing customer accounts, and leading to regulatory fines.
Financial institutions must proactively implement ransomware protection strategies, including regular data backups, endpoint security measures, and employee training to recognize suspicious activity.
4. Supply Chain Vulnerabilities
Many financial institutions rely on third-party vendors, cloud services, and fintech partners to streamline operations. However, these third-party connections create additional cybersecurity risks. A single weak link in the supply chain can expose an entire financial system to cyber threats.
A prime example occurred in 2020 when a global payment processing company suffered a cyberattack that compromised millions of credit card transactions worldwide. This breach underscored the importance of vetting third-party security practices.
Source: Elastico
How Financial Institutions Are Strengthening Cybersecurity
1. Implementing Zero Trust Security Models
The Zero Trust framework assumes that every user, device, and network access request could be a potential security risk. Instead of relying on traditional perimeter-based security, financial institutions are adopting multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access controls, and continuous monitoring to verify users and prevent unauthorized access.
2. Enhancing Cloud Security
With the increasing adoption of cloud-based banking and digital services, financial firms must secure cloud environments against cyber threats. Strategies such as encryption, data tokenization, and intrusion detection systems help protect customer data and maintain regulatory compliance.
3. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning for Fraud Detection
Financial institutions are leveraging AI-powered cybersecurity to detect anomalies, prevent fraud, and automate threat response. Machine learning algorithms analyze transaction patterns in real time, flagging suspicious activity and minimizing financial fraud.
For instance, many banks now use AI-driven fraud detection systems that can identify unauthorized transactions and freeze accounts before fraudulent activities escalate.
4. Strengthening Regulatory Compliance and Cybersecurity Policies
Governments and regulatory bodies have introduced stricter cybersecurity regulations to safeguard the financial sector. Some key regulations include:
| Cybersecurity Measure | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Zero Trust Security Model | Requires verification for every access request | Minimizes unauthorized access and insider threats |
| AI-Powered Fraud Detection | Uses machine learning to detect fraudulent activities | Enhances fraud prevention and real-time security |
| Blockchain Technology | Provides a decentralized and tamper-proof transaction ledger | Reduces fraud risks and improves transparency |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to security regulations (GDPR, PCI DSS, Basel III) | Avoids penalties and ensures data security |
| Biometric Authentication | Uses fingerprints, facial recognition, and voice ID for access | Improves security and reduces reliance on passwords |
Banks and fintech firms must comply with these regulations to avoid penalties and maintain customer trust.
5. Employee Training and Cybersecurity Awareness
Human error remains one of the leading causes of cybersecurity breaches. To combat this, financial institutions are investing in employee cybersecurity training programs that educate staff on phishing attacks, password hygiene, and secure handling of financial data.
Banks also conduct simulated cyberattack exercises to test their security preparedness and response times.
The Future of Cybersecurity in Finance
1. Biometric Authentication and Passwordless Security
As cyber threats evolve, biometric authentication methods such as fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice recognition are becoming standard in financial security. Many mobile banking apps now incorporate biometric verification to enhance account security.
2. Blockchain for Secure Transactions
Blockchain technology is being explored as a secure, tamper-proof ledger for financial transactions. By decentralizing transaction records, blockchain reduces the risk of fraud and unauthorized alterations.
3. Cybersecurity Insurance for Financial Institutions
With cyberattacks on the rise, many financial firms are investing in cybersecurity insurance to mitigate financial losses from data breaches, ransomware attacks, and fraud.
4. Quantum Computing and Financial Security
While quantum computing holds promise for faster data processing, it also presents potential risks to encryption security. Financial institutions are already exploring quantum-resistant cryptographic methods to safeguard data against future threats.
Emerging Cybersecurity Technologies in Finance
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, financial institutions are adopting new technologies to stay ahead of threats. Some of the key emerging cybersecurity technologies include:
- Secure Access Service Edge (SASE): A cloud-based security framework integrating networking and security functions for enhanced threat protection.
- Extended Detection and Response (XDR): A cybersecurity approach that consolidates multiple security products into a unified threat detection and response system.
- Behavioral Biometrics: A technology that analyzes user behavior patterns, such as typing speed and mouse movements, to detect fraud.
The Role of Government Collaboration in Strengthening Financial Security
Financial institutions alone cannot combat cyber threats; governments play a crucial role in cybersecurity initiatives. Collaboration between financial entities and governments ensures:
- Stronger cybersecurity policies and frameworks
- Enhanced intelligence sharing on cyber threats
- Stricter enforcement of cybersecurity regulations
Initiatives like the Cybersecurity Information Sharing Act (CISA) in the U.S. and the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA) help financial institutions mitigate risks through coordinated efforts.
Conclusion
Cybersecurity in finance is no longer an option—it’s a necessity. As digital transactions, open banking, and fintech innovation continue to reshape the financial landscape, financial institutions must remain proactive in cybersecurity measures to protect customer assets, sensitive data, and industry stability.
By implementing zero-trust security models, AI-driven fraud detection, blockchain technology, and biometric authentication, the financial sector can mitigate cyber risks and enhance digital trust. In a world where cyber threats are becoming more sophisticated, financial institutions must stay one step ahead to safeguard their customers and maintain a secure financial services industry.
About The Author
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Related Business Articles





